ESP32: Laboratorios: mudanças entre as edições
Sem resumo de edição |
|||
| Linha 278: | Linha 278: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="c"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="c"> | ||
/* | /* | ||
Basic test program, send date | Basic test program, send date with LoRa. | ||
https://github.com/Heltec-Aaron-Lee/WiFi_Kit_series | https://github.com/Heltec-Aaron-Lee/WiFi_Kit_series | ||
*/ | */ | ||
| Linha 343: | Linha 337: | ||
/* | /* | ||
Check the new incoming messages, and print via serialin 115200 baud rate. | Check the new incoming messages, and print via serialin 115200 baud rate. | ||
https://github.com/Heltec-Aaron-Lee/WiFi_Kit_series | https://github.com/Heltec-Aaron-Lee/WiFi_Kit_series | ||
*/ | */ | ||
| Linha 356: | Linha 344: | ||
char message[20]; | char message[20]; | ||
void lora(){ | void lora(){ | ||
Edição das 19h11min de 8 de fevereiro de 2022
ESP32: Laboratórios
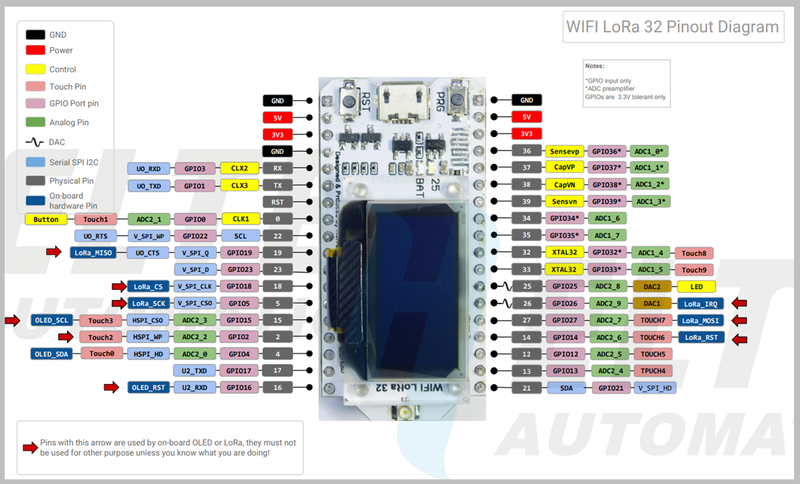
A placa Heltec ESP32 LoRa é uma placa de desenvolvimento que integra três formas distintas de comunicação: Wifi, Bluetooth e a rede de comunicação de longo alcance LoRa. Além disto a placa apresenta um display OLED, o que facilita o controle da operação do dispositivo localizado em locais remotos.
- Referências sobre o Heltec ESP32
- Heltec ESP32+LoRa Series Quick Start: https://heltec-automation-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/esp32/quick_start.html
- Instalação da placa do Heltec ESP32 com a IDE do Arduino
- IDE -> Arquivo -> Preferências
- URLs Adicionais para Gerenciadores de Placa: https://github.com/Heltec-Aaron-Lee/WiFi_Kit_series/releases/download/0.0.5/package_heltec_esp32_index.json
- Ferramentas -> Gerenciadores de Placa -> Instalar Heltec ESP32 Series Dev/boards
- Selecionar placa WiFi LoRa 32
Laboratório 1: Wifi
Exemplo pronto da biblioteca padrão do Arduino: Arquivo -> Exemplos -> Wifi -> SimpleWifiServer:
- Configurar apenas ssid e passwd da rede Wifi;
- Identificar via terminal serial o endereço IP recebido pelo ESP32;
- Será possível controlar led (gpio 5, ou outro) via nagerador Web.
Laboratório 2: Bluetooth
Exemplo pronto da biblioteca padrão do Arduino: Arquivo -> Exemplos -> BluetoothSerial -> SerialToSerialBT:
- Exemplo de interação bluetooth entre ESP32 e Android Serial Bluetooth Terminal.
- Carregar código no ESP32;
- Instalar aplicativo Serial Bluetooth Terminal no Android;
- Parear o ESP32 com o Android;
- Trocar mensagens seriais entre o terminal do ESP32 e o aplicativo Serial Bluetooth Terminal
Laboratório 3: Bluetooth Low Energy - BLE
Ver detalhes do BLE: https://randomnerdtutorials.com/esp32-bluetooth-low-energy-ble-arduino-ide/.
- Biblioteca: https://github.com/nkolban/ESP32_BLE_Arduino
- Exemplo pronto Arquivo -> Exemplos -> ESP BLE Arduino -> BLEserver;
- Instalar aplicativo BLE Terminal no Android;
- Conectar ao dispositivo.
Laboratório 4: Servidor Web e Display OLED
Exemplo de Web Server construído a partir de dois exemplos prontos:
- Wifi: busca de redes e conexão baseadas no exemplo:
Arquivo -> Exemplos -> Heltec ESP Dev-Boards -> Factory_Tests -> WIFI_Kit_32_Factory_Test
- Servidor Web: baseado no exemplo:
Arquivo -> Exemplos -> Wifi -> SimpleWiFiServer
Código
/*
* Web Server
*
* Wifi: busca de redes e conexão baseadas no exemplo:
* Arquivo -> Exemplos -> Heltec ESP Dev-Boards -> Factory_Tests -> WIFI_Kit_32_Factory_Test
*
* Servidor Web: baseado no exemplo:
* Arquivo -> Exemplos -> Wifi -> SimpleWiFiServer
*/
#include "heltec.h"
#include "WiFi.h"
#include "images.h"
WiFiServer server(80);
void logo(){
Heltec.display -> clear();
Heltec.display -> drawXbm(0,5,HelTec_LOGO_width,HelTec_LOGO_height,(const unsigned char *)HelTec_LOGO_bits);
Heltec.display -> display();
delay(1000);
Heltec.display->clear();
}
void wifi_logo(){
Heltec.display -> clear();
Heltec.display->drawXbm(34, 19, WiFi_Logo_width, WiFi_Logo_height, WiFi_Logo_bits);
Heltec.display -> display();
delay(1000);
Heltec.display->clear();
}
void WIFISetUp(void)
{
// Set WiFi to station mode and disconnect from an AP if it was previously connected
WiFi.disconnect(true);
delay(1000);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
WiFi.setAutoConnect(true);
WiFi.begin("SSID","passwd");
delay(100);
byte count = 0;
while(WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED && count < 10)
{
count ++;
if (count == 1) Serial.println("Connecting...");
delay(500);
Heltec.display->clear();
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 0, "Connecting...");
Heltec.display -> display();
}
Heltec.display -> clear();
if(WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECTED)
{
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 0, "Connecting...OK.");
Heltec.display -> display();
delay(500);
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 10, "IP address: ");
Heltec.display -> display();
delay(500);
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 20, WiFi.localIP().toString());
Heltec.display -> display();
delay(2000);
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
}
else
{
Heltec.display -> clear();
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 0, "Connecting...Failed");
Heltec.display -> display();
Serial.println("Connecting...Failed");
// while(1);
}
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 40, "WIFI Setup done");
Heltec.display -> display();
Serial.println("WIFI Setup done");
delay(500);
Heltec.display->clear();
}
void WIFIScan(void)
{
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 20, "Scan start...");
Heltec.display -> display();
Serial.println("Scan start...");
int n = WiFi.scanNetworks();
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 30, "Scan done");
Heltec.display -> display();
Serial.println("Scan done");
delay(500);
Heltec.display -> clear();
if (n == 0)
{
Heltec.display -> clear();
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 0, "no network found");
Heltec.display -> display();
Serial.println("No network found");
while(1);
}
else
{
Serial.print(n);
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 0, (String)n);
Heltec.display -> drawString(14, 0, "networks found:");
Heltec.display -> display();
Serial.print(n);
Serial.println(" networks found:");
delay(500);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
// Print SSID and RSSI for each network found
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, (i+1)*9,(String)(i + 1));
Heltec.display -> drawString(6, (i+1)*9, ":");
Heltec.display -> drawString(12,(i+1)*9, (String)(WiFi.SSID(i)));
Heltec.display -> drawString(90,(i+1)*9, " (");
Heltec.display -> drawString(98,(i+1)*9, (String)(WiFi.RSSI(i)));
Heltec.display -> drawString(114,(i+1)*9, ")");
// display.println((WiFi.encryptionType(i) == WIFI_AUTH_OPEN)?" ":"*");
Serial.print(i+1);
Serial.print(" : ");
Serial.print(WiFi.SSID(i));
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(WiFi.RSSI(i));
Serial.println(")");
delay(10);
}
}
Heltec.display -> display();
delay(800);
Heltec.display -> clear();
}
void setup()
{
pinMode(LED,OUTPUT);
Heltec.begin(true /*DisplayEnable Enable*/, false /*LoRa Enable*/, true /*Serial Enable*/);
logo();
wifi_logo();
WIFIScan();
WIFISetUp();
//WiFi.disconnect(true);//重新初始化WIFI
//delay(1000);
//WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
//WiFi.setAutoConnect(true);
server.begin();
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 0, "Waiting Web Clients");
Heltec.display -> display();
}
void loop(){
WiFiClient client = server.available(); // listen for incoming clients
if (client) { // if you get a client,
Serial.println("New Client."); // print a message out the serial port
Heltec.display -> clear();
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 0, "New Web Client");
Heltec.display -> display();
String currentLine = ""; // make a String to hold incoming data from the client
while (client.connected()) { // loop while the client's connected
if (client.available()) { // if there's bytes to read from the client,
char c = client.read(); // read a byte, then
Serial.write(c); // print it out the serial monitor
if (c == '\n') { // if the byte is a newline character
// if the current line is blank, you got two newline characters in a row.
// that's the end of the client HTTP request, so send a response:
if (currentLine.length() == 0) {
// HTTP headers always start with a response code (e.g. HTTP/1.1 200 OK)
// and a content-type so the client knows what's coming, then a blank line:
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Content-type:text/html");
client.println();
// the content of the HTTP response follows the header:
client.print("Click <a href=\"/H\">here</a> to turn the LED on.<br>");
client.print("Click <a href=\"/L\">here</a> to turn the LED off.<br>");
// The HTTP response ends with another blank line:
client.println();
// break out of the while loop:
break;
} else { // if you got a newline, then clear currentLine:
currentLine = "";
}
} else if (c != '\r') { // if you got anything else but a carriage return character,
currentLine += c; // add it to the end of the currentLine
}
// Check to see if the client request was "GET /H" or "GET /L":
if (currentLine.endsWith("GET /H")) {
digitalWrite(LED, HIGH); // GET /H turns the LED on
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 10, "Turn LED on");
Heltec.display -> display();
}
if (currentLine.endsWith("GET /L")) {
digitalWrite(LED, LOW); // GET /L turns the LED off
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 10, "Turn LED off");
Heltec.display -> display();
}
}
}
// close the connection:
client.stop();
Serial.println("Client Disconnected.");
}
}
Laboratório 5: LoRa Emissor e Receptor
Exemplo de comunicação LoRa baseado em dois exemplos prontos:
Arquivo -> Exemplos -> Heltec ESP Dev-Boards -> LoRa -> LoraSender Arquivo -> Exemplos -> Heltec ESP Dev-Boards -> LoRa -> LoraReceiver
Aos exemplos prontos foi acrescentada a biblioteca images.h para mostrar a comunicação no Display OLED.
- Emissor LoRa
/*
Basic test program, send date with LoRa.
https://github.com/Heltec-Aaron-Lee/WiFi_Kit_series
*/
#include "heltec.h"
#define BAND 433E6 //you can set band here directly,e.g. 868E6,915E6
#include "images.h"
void lora(){
Heltec.display -> clear();
Heltec.display -> drawXbm(34, 19, LoRa_Logo_width, LoRa_Logo_height, LoRa_Logo_bits);
Heltec.display -> display();
delay(2000);
Heltec.display->clear();
}
int counter = 0;
void setup() {
//WIFI Kit series V1 not support Vext control
Heltec.begin(true /*DisplayEnable Enable*/, true /*Heltec.LoRa Disable*/, true /*Serial Enable*/, true /*PABOOST Enable*/, BAND /*long BAND*/);
lora();
LoRa.setSyncWord(0xF3);
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Sending packet: ");
Serial.println(counter);
Heltec.display -> clear();
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 0, "Sending packet: ");
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 10,(String)(counter));
Heltec.display -> display();
// send packet
LoRa.beginPacket();
/*
* LoRa.setTxPower(txPower,RFOUT_pin);
* txPower -- 0 ~ 20
* RFOUT_pin could be RF_PACONFIG_PASELECT_PABOOST or RF_PACONFIG_PASELECT_RFO
* - RF_PACONFIG_PASELECT_PABOOST -- LoRa single output via PABOOST, maximum output 20dBm
* - RF_PACONFIG_PASELECT_RFO -- LoRa single output via RFO_HF / RFO_LF, maximum output 14dBm
*/
LoRa.setTxPower(20,RF_PACONFIG_PASELECT_PABOOST);
LoRa.print("hello ");
LoRa.print(counter);
LoRa.endPacket();
counter++;
digitalWrite(25, HIGH); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
delay(1000); // wait for a second
digitalWrite(25, LOW); // turn the LED off by making the voltage LOW
delay(1000); // wait for a second
}
- Receptor LoRa
/*
Check the new incoming messages, and print via serialin 115200 baud rate.
https://github.com/Heltec-Aaron-Lee/WiFi_Kit_series
*/
#include "heltec.h"
#include "images.h"
char message[20];
void lora(){
Heltec.display -> clear();
Heltec.display -> drawXbm(34, 19, LoRa_Logo_width, LoRa_Logo_height, LoRa_Logo_bits);
Heltec.display -> display();
delay(2000);
Heltec.display->clear();
}
#define BAND 433E6 //you can set band here directly,e.g. 868E6,915E6
void setup() {
//WIFI Kit series V1 not support Vext control
Heltec.begin(true /*DisplayEnable Enable*/, true /*Heltec.LoRa Disable*/, true /*Serial Enable*/, true /*PABOOST Enable*/, BAND /*long BAND*/);
lora();
LoRa.setSyncWord(0xF3);
}
void loop() {
// try to parse packet
int packetSize = LoRa.parsePacket();
if (packetSize) {
// received a packet
Serial.print("Received packet '");
// read packet
char c;
int i = 0;
while (LoRa.available()) {
c = (char)LoRa.read();
Serial.print(c);
message[i] = c;
i++;
//sprintf(message, LoRa.read())
}
// print RSSI of packet
Serial.print("' with RSSI ");
Serial.println(LoRa.packetRssi());
Heltec.display -> clear();
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 0, "Received packet: ");
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 10, (String)message);
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 20, "RSSI: ");
Heltec.display -> drawString(0, 30, (String)LoRa.packetRssi());
Heltec.display -> display();
}
}
Referências
Evandro.cantu (discussão) 15h48min de 8 de fevereiro de 2022 (-03)